OUR HEALTH DESTINY- Infectious diseases; tiny but ferocious
- Shehryar Zeeshan

- Dec 14, 2020
- 7 min read
Updated: May 31, 2022
Dear audience,
I believe that you should learn every day something new! keep your brain busy and let its imagination brushfire! make yourself happy but at the same time active. In this blog I want to show you something tiny but in the terms of ferociousness it is majestic. That is just fancy and abstract description for these tiny extraterrestrials, or rather should I analyse that they are not even creatures they are half-alive and half-dead, these dangerous and captivating beings have mind boggled and perplexed scientists for centuries if not Millenniums. I am talking about viruses.
Being a student of Beacon house school system we have explored this mysterious and anomalous beings, in detail and the fundamental lesson I learnt from all that project-based learning was basically Unity. There were many other lessons hidden in the project as well but the main lesson was Unity. The project-based learning was about research on the different infectious diseases which caused great loss to human lives in history, observations regarding the spread of these diseases which may start as endemic or outbreak resulting in epidemics and pandemics, the awareness campaign was the basic reason for this project to make people aware that these hazardous diseases can be a threat that is unimaginable.
By the end of the project, we were organizing an “Awareness Campaign” to help the community to learn how they can control the spread of infectious diseases hence stopping it to become an epidemic/pandemic this project-based learning evoked our skills about knowledge, collaboration, creativity, critical thinking and presentation.
If we Talk about infectious diseases in general, they are basically disorders caused by microorganisms or organisms. The examples of microorganisms are Bacteria, Protozoa, Fungi, viruses or parasites. Every disease has its own specific signs and symptoms. Let's take COVID-19 for example: dear audience, here I have attached a poster made by myself. So read it and enjoy it!

Dear audience now let me explain each and every step in detail, and let me guide you through this amazing journey project-based learning by the way I am Explaining and creating awareness of infectious diseases by guiding you through the project-based learning is only because I believe that it is the best way, to evoke the 21st-century skills. But later in the blog, I will also explain my own learning and my own point of view on the project-based learning:
1. Driving Question/ collection of the reflections:
The first step was thinking about a D.Q. That is driving question, the whole point of view the topic or the crux in a nutshell I would explain the driving question as a match of influential ideas that can revolutionize or can have a major impact on all over the world, it can Ignite imagination but not only imagination it can take us through a Misty-full adventurous 21st century:
My driving question was: "Infectious Diseases; tiny but ferocious!" so you get the whole point of view right? It explains the topic in a nutshell and it does not have any generic words in it, so I believe that it was a perfect driving question.
2. Timeline:
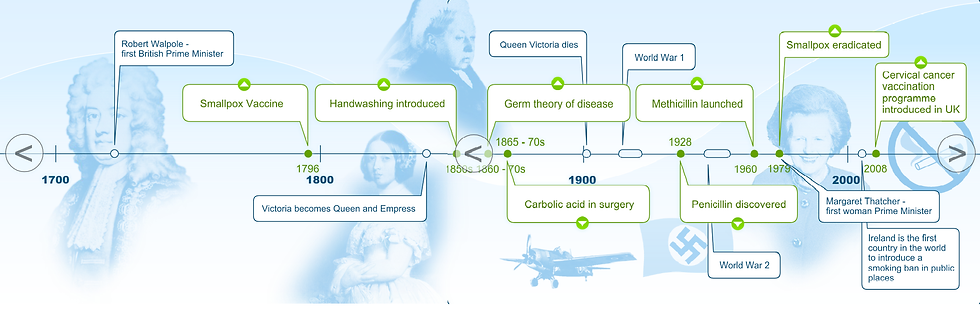
The second step was making a timeline, critical thinking and creativity is here. I am sharing a link where I made my home timeline, I will hopefully embed it in this blog so you can view it. I researched for 10 infectious diseases which spread as epidemic or pandemic in the world.

3. Poster making/ Presentation:
Third step was Research on specific area of the disease prescribed to me. I Presented my work in the form of posters. My Poster carried research with content and pictures/diagrams/drawings. This task tested my presentational skills. I researched on the disease known as tuberculosis, here you can find some of my done research on tuberculosis and my colourful poster on tuberculosis hope you enjoy it.
Research:
History of tuberculosis. In 1867, tuberculosis (TB) was the leading cause of death in Canada. The bacterium that causes TB, the tubercle bacillus, was discovered by a German scientist, Robert Koch, in 1882. History of TB in Ancient Times The earliest historical references to TB in Egypt are in a medical papyrus dated to 1550 BC. 5 Among Egyptian mummies spinal tuberculosis, one particular type of TB, known as Pott's disease has been detected. TB has also been identified from India in a Sanskrit hymn (Rig Veda) which has been dated to 1550 BC. People with TB disease are most likely to spread it to people they spend time with every day. This includes family members, friends, and coworkers or schoolmates. Learn about latent TB infection and TB disease. Page last reviewed: March 11, 2016. Content source: Division of Tuberculosis Elimination. Throughout history, the disease tuberculosis has been variously known as consumption, phthisis and the White Plague. It is generally accepted that the causative agent, Mycobacterium tuberculosis originated from other, more primitive organisms of the same genus Mycobacterium. In 2014, results of a new DNA study of a tuberculosis genome reconstructed from remains in southern Peru suggest that human tuberculosis is less than 6,000 years old. Even if researchers theorise that humans first acquired it in Africa about 5,000 years ago,[1] there is evidence that the first tuberculosis infection happened about 9,000 years ago.[2] It spread to other humans along trade routes. It also spread to domesticated animals in Africa, such as goats and cows. Seals and sea lions that bred on African beaches are believed to have acquired the disease and carried it across the Atlantic to South America. Hunters would have been the first humans to contract the disease there.
Infection: An infection is the invasion of an organism's body tissues by disease-causing agents, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agents and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection.

What’s the difference between a pandemic, an epidemic, endemic, and an outbreak?
AN EPIDEMIC is a disease that affects a large number of people within a community, population, or region.
A PANDEMIC is an epidemic that’s spread over multiple countries or continents.
ENDEMIC is something that belongs to a particular people or country.
AN OUTBREAK is a greater-than-anticipated increase in the number of endemic cases. It can also be a single case in a new area. If it’s not quickly controlled, an outbreak can become an epidemic.
4. PBL/ DIY:
The fourth step was to make a project-based learning do it yourself tutorial on how to make a mask and a sanitizer so you can find my video on the given link on youtube.com and do subscribe to my channel that is the Twilight zone with Shehryar Zeeshan:

5. Modes of transmission:
The fifth step was to explain the modes of transmission through diagrams, so dear audience you can find my diagram attached here study it and hopefully you will find it interesting and learn something new from it:

What are the types of diseases?
Infectious diseases: These are the diseases caused by an outside organism. This organism can be a bacterium like protozoa, fungi or even viruses. Sometimes they can be caused by parasites like Ascaris, nematodes which survive in the human body for years.
Diseases are disorders that affect either a part of, or the entire body by hindering bodily functions. Diseases can be caused due to infectious or non-infectious causes. Non-infectious causes are generally due to internal factors, genetic abnormalities, while infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms.
What are the different modes of transmission of diseases (pathogens)?
Direct transmission
Direct contact: Infectious diseases are transmitted from person to person by direct or indirect contact. Certain types of viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi can all cause infectious disease.
Droplet infection: A respiratory droplet is a small aqueous droplet produced by exhalation, consisting of saliva or mucus and other matter derived from respiratory tract surfaces.
Contact with soil: Many fungi thrive in high humidity, especially when the leaves are wet for long periods. Rain can also splash disease spores from the soil up onto the leaves, or spread spores from lower infected leaves to healthy leaves up higher on the plant. That's one reason why some diseases start on lower leaves and spread upwards.
Inoculation to skin or to mucosa: Inoculation into skin or mucosa: Disease agents may be directly inoculated into the skin or mucosa, e.g. dog bite, contaminated needles, syringes. Transplacental: Transmitted from mother to child; to whom such substances may be dangerous. This would include, for example, HIV.
Indirect transmission
Vehicle borne: indirect transmission of an infectious agent that occurs when a vehicle (or fomite).
Vehicle is an object that in this sense is used to transmit any disease it can be fomite that are clothes or any organism that has got the disease from another organism will transfer it to any third organism.
Vector-borne: Mechanical or biological.
Vector is an organism that has got a disease on its own from a microorganism or from any other organism for example a Protozoa on or a bacteria. Vector can transfer a disease to another organism that is not affected biologically. Mechanical transmission is facilitated by a mechanical vector, an animal that carries a pathogen from one host to another without being infected itself.
Airborne: An airborne disease is any disease that is caused by pathogens that can be transmitted through air. Some infectious agents can travel long distances and remain suspended in the air for an extended period of time. These types of diseases when are suspended in the air, consequently we catch them. Fomite - borne: Fomites are motionless substances other than water or food contaminated by the infectious discharges from a patient and capable of withholding and transferring infectious agent to a healthy person. Fomites includes soiled clothes, toys, towels, linen, cups, spoons, pencils, books, surgical dressing, etc., Diseases transmitted by fomites are typhoid, diphtheria, and skin infections.
Unclean hands and fingers: Unclean hands and fingers - Hands are the most common medium by which pathogenic representatives are transferred to food from the skin, nose, bowel, etc., as well as from other food.
6. My reflection:
The sixth step is to present your reflection about overall project-based learning.

Hope you all enjoyed my Blog on PBL.
Regards,
Shehryar Zeeshan.
BMI-B
BSS
BSU




Comments